Lesson 3 – Inequalities
Student Workbook Solutions (Beta Lesson 3)
Test Solutions (Beta Lesson 3)
Circle your answer.
-
(3^(0))(3^(-2))(3^(2))= \left(3^{0}\right)\left(3^{-2}\right)\left(3^{2}\right)=
A. 3
B. 1
C. 9
D. 0 -
y^(8)-:y^(2)=quad(y!=0) y^{8} \div y^{2}=\quad(y \neq 0)
A.y^(6) y^{6}
B.y^(4) y^{4}
C.y^(10) y^{10}
D.(1)/(y^(6)) \frac{1}{y^{6}} -
(3q^(2))^(3)= \left(3 q^{2}\right)^{3}=
A.3q^(6) 3 q^{6}
B.3q^(5) 3 q^{5}
C.9q^(6) 9 q^{6}
D.27q^(6) 27 q^{6} -
(P^(3)N^(-2))/(N^(2)P^(4))= \frac{\mathrm{P}^{3} \mathrm{~N}^{-2}}{\mathrm{~N}^{2} \mathrm{P}^{4}}=
A.P^(-1) \mathrm{P}^{-1}
B.(P)/(N^(4)) \frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{N}^{4}}
C.(1)/(N^(4)P) \frac{1}{N^{4} P}
D.N^(4)P^(-1) \mathrm{N}^{4} \mathrm{P}^{-1} -
If
3^(Y-1)=81 3^{Y-1}=81 Y Y
A. 5
B. 4
C. 3
D. 2 -
If
X X X^(5) X^{5}
A. 0
B. -1
C. 16
D. 32 -
The greatest common factor of
A^(2)B^(4)+B^(3)A A^{2} B^{4}+B^{3} A
A.AB^(3) A B^{3}
B.AB A B
C.A^(2)B A^{2} B
D.A^(3)B A^{3} B -
Factoring out the greatest common factor from
P^(2)Q+P^(4)Q^(2) \mathrm{P}^{2} \mathrm{Q}+\mathrm{P}^{4} \mathrm{Q}^{2}
A.QP^(2) Q P^{2}
B.Q+P \mathrm{Q}+\mathrm{P}
C.P+Q^(2) P+Q^{2}
D.1+P^(2)Q 1+\mathrm{P}^{2} \mathrm{Q} (-2+4)^(-2)= (-2+4)^{-2}=
A. -4
B.-1//4 -1 / 4
C.1//4 1 / 4
D. 4 -
If
3^(6)=9^(X),X= 3^{6}=9^{X}, X=
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Questions 1-10 on each test cover new concepts that must be mastered before moving on to the next lesson. Questions 11-15 cover concepts learned in previous courses or in previous lessons of Algebra 2. You may use these questions as a review tool.
-
If
X+2Y=5 X+2 Y=5 X=1//2Y X=1 / 2 Y Y= Y=
A. 2
B.1//2 1 / 2
C. 1
D. -2 -
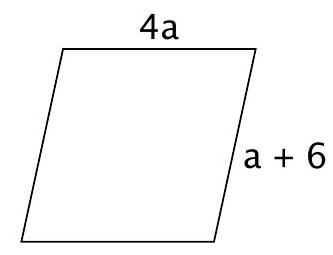
In the rhombus shown, what is the value of
a a
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
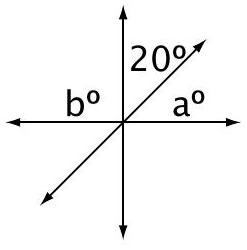
- Three intersecting lines are shown. What is the value of
b+a b+a
A. 170
B. 160
C. 140
D. 70
-
A recipe requires three eggs and seven cups of flour. If 15 eggs are used, how many cups of flour are needed?
A. 5
B. 19
C. 25
D. 35 -
What is the slope of a line that passes through the origin and the point
(-3,-2) (-3,-2)
A.2//3 2 / 3
B.-2//3 -2 / 3
C.3//2 3 / 2
D.-3//2 -3 / 2
